Carbon Capture Utilisation and Storage (CCUS)
The 2016 Paris climate deal set targets of maintaining the global temperature rise well under 2C, to prevent the worst effects of climate change. Several jurisdictions have also announced targets of reaching net-zero emissions by 2050.
In order to reach these targets, the world’s leaders must make efforts to tackle atmospheric pollution, especially carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, which are considered to be the biggest contributor towards climate change acceleration. Emissions must be cut by around 50% in order to make a difference.
In 2021, the European Union adopted ambitious new targets to curb climate change, with a pledge to make them legally binding. Under a new law, the bloc committed to cutting carbon emissions by at least 55% by 2030, compared with 1990 levels. The plans set a limit on the levels of CO2 removal that can count towards the 2030 target to ensure that states actively lower emissions rather than removing them from the atmosphere through forests, for example.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is emitted by a wide array of sources, from power generation and heavy industry to domestic heating and private vehicles. One method for CO2 removal is the implementation of Carbon Capture Utilisation & Storage (CCUS), which has the potential to cut carbon dioxide emissions from the world’s heavy industries by 50% – working in tandem with renewable energy and energy efficiency practices.
If deployed quickly and effectively, this could lead to sustainable net-zero energy consumption and have a significant impact on slowing climate change.
Lead contact:
Ole Rygg
Managing Director Wells
What is CCUS?
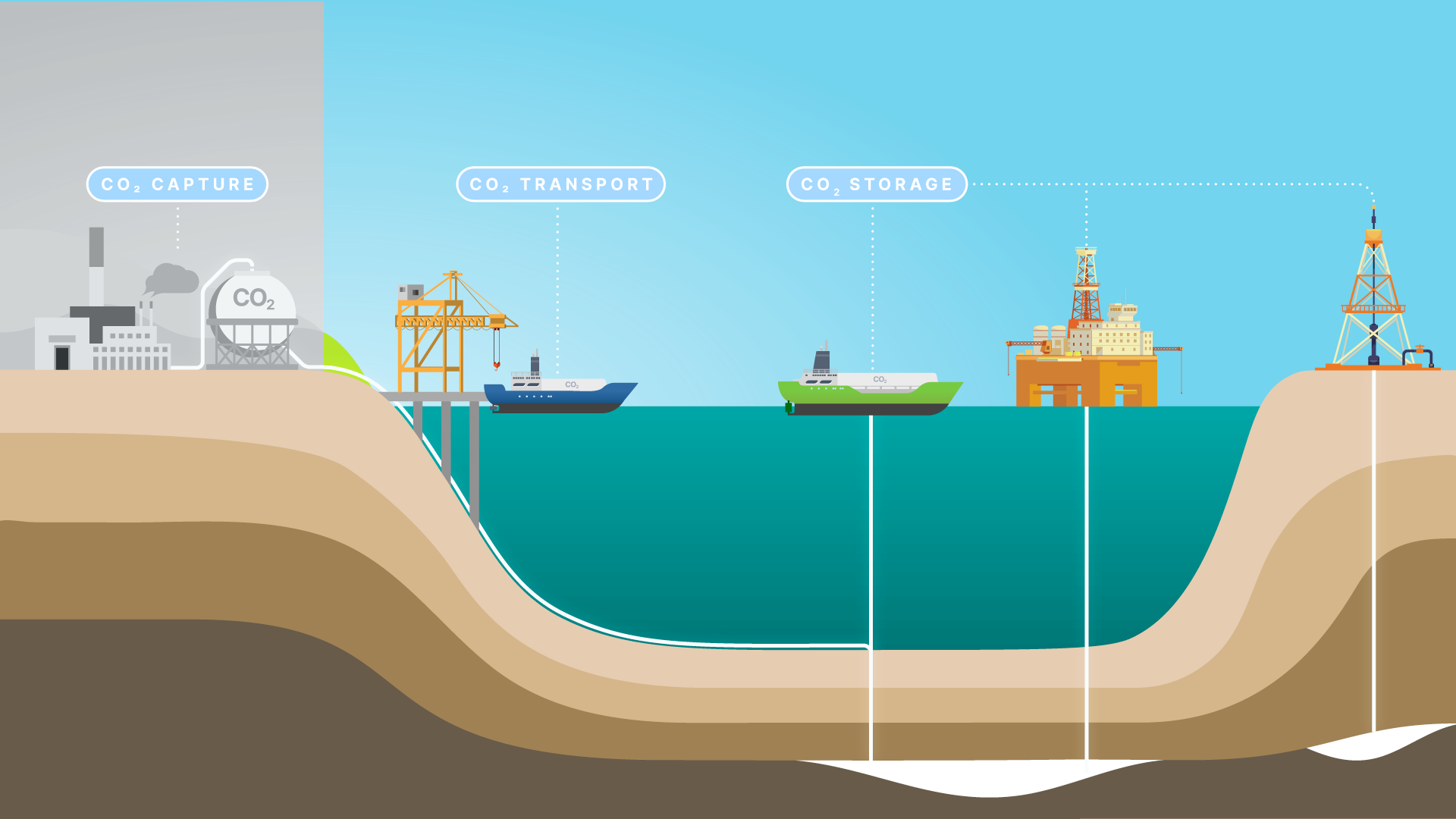
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) is a method and technology for the removal of CO2 emissions produced from the use of fossil fuels for electricity generation, with the potential to prevent the dispersal of potentially 90% of harmful emissions.
How does it work?
The technology works by capturing carbon dioxide emissions from flue exhausts, converting the gas into liquid form before transporting by pipeline or ship and storing safely and permanently far below the Earth’s surface – replicating nature’s storage of oil and gas – or through conversion into useful chemicals used in oil extraction or remediation of industrial waste.
The use of CCS with renewable biomass is one of the few carbon abatement technologies that can be used in a ‘carbon-negative’ mode – actually taking carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere.

Challenges with “going green”
Transitioning to net-zero on a company scale can be just as intimidating as the bigger national picture. Often, kickstarting a decarbonisation journey can be the toughest step, with challenges including:
- Difficulty identifying suitable carbon reduction and clean energy solutions for your business
- How to successfully and cost-effectively reduce carbon footprint for existing infrastructure
- A limited understanding of the risk profile associated with energy transition and suitable mitigation techniques
- Lack of in-house expertise and capabilities to assess and successfully implement sustainable solutions
- Limited understanding of requirements to ensure compliance with regulations and legislation
- Difficulty in determining the actual projected revenue that will be acquired through energy transition initiatives
Our services
ABL is investing heavily in solutions applicable to carbon neutrality, renewable energy, and hydrogen power. Through group company AGR, we provide services to assess, evaluate, and support the implementation of your carbon reduction initiatives through proven processes and independent verification.
- Technical and commercial “green energy” feasibility studies (cost-benefit analysis)
- Review of existing infrastructure to determine options to reduce carbon footprint
- CO2 flow modelling and injectivity and reservoir simulations of underground storage
- Application of relief well drilling technology to make closed-loop geothermal wells
- Heat capacity simulations for closed loop geothermal wells
- Well integrity assessment of existing field for underground CO2 storage
- Geoscientific appraisal of the ground conditions to assess drilling hazards and suitability of ground for well and infrastructure foundations
- Design, engineering, construction, installation and management of carbon injection and geothermal wells
- Regulatory compliance and approval consulting for underground CO2 storage and geothermal wells
- Due diligence, audits, and certification of “green energy” implementation
- Safety case development and reviews for CO2 and H2 facilities and vessels
- Asset management strategy
- Maintenance, integrity and inventory management regime development and optimization
AGR’s Experience
Viable Options – A conclusive business case detailing feasible decarbonisation strategies for your business
Investment Strategy – Gain a clear understanding of the investment requirements for carbon reduction and how they can be optimised
Project Sanction – Identify viable options to reduce carbon emissions to get new projects sanctioned and optimize investment
Compliance Assurance – Assure compliance with international standards relating to integrity, decarbonisation and asset management
Cost and Time Efficiencies – Rely on experts to deliver a cost and time-effective solution for kick-starting or accelerating your decarbonisation journey without impacting day-to-day operations
Safety Integrity – Develop and implement decarbonisation tactics that assure safety integrity through the use of proven processes
Click here for more information on AGR’s CCUS expertise.
Case Study
Co-development of a Co2 Capture and Storage (CCS) Hub
The goals of the deepC Store Project align with the Australian government’s Low Emissions Technology Statement, with carbon capture and storage being identified as one of the five priority technologies and economic stretch goals to reduce emissions from energy, transport, agriculture, and heavy industry.